Understanding Laboratory Ventilation Controls
There are several different types of ventilation controls available in laboratories, each offering specific protections when used properly. These include chemical fume hoods, biosafety cabinets, and laminar flow hoods.
Read more about how each unit functions, what protection they offer, and what happens to the contaminated air.
A visual summary is available here.
Chemical Fume Hoods
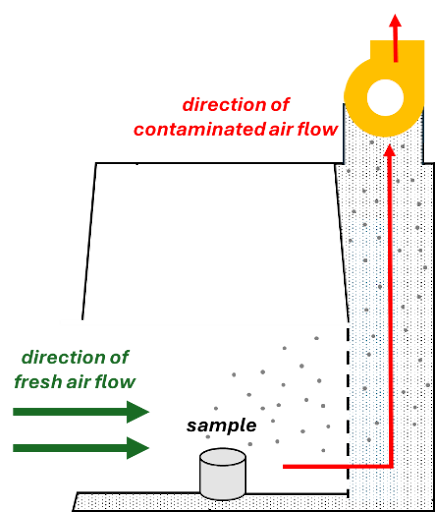
Chemical fume hoods are used for handling hazardous materials. Fume hoods pull fresh air in from the laboratory ensuring that hazardous fumes are moved away from the user. These hazardous fumes are then exhausted through the building ventilation, ensuring that no contaminated air is recirculated back into the laboratory space.
Fume hoods offer excellent protection for the user but do not protect the sample from contamination and they cannot be used for biohazardous materials.
SafetyNet #35 How to Use a Chemical Fume Hood Safely offers additional insights into using a chemical fume hood properly.
Biosafety Cabinets
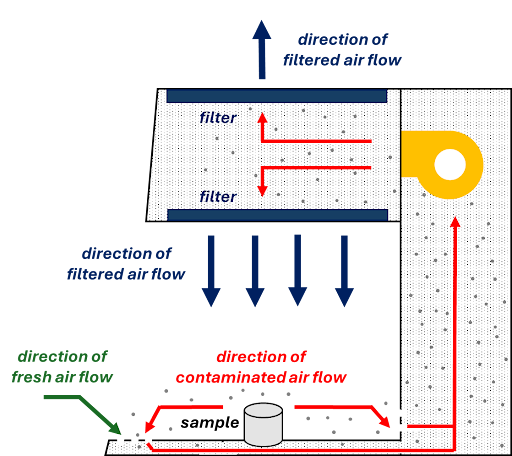
Biosafety cabinets (BSCs) are used for handling infectious microorganisms and biohazardous materials. BSCs also pull in fresh air from the laboratory to ensure the user is not contaminated; however, the air goes through a filter before it is released into the BSC, ensuring the sample is in a sterile environment. All contaminated air is filtered before being recirculated back into the BSC or exhausted into the room.
BSCs offer both user and sample protection, but they are limited to handling infectious microorganisms and biohazardous materials; BSCs are not suitable for handling hazardous materials.
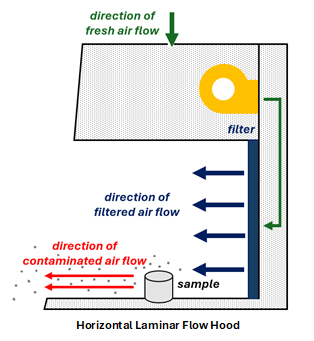
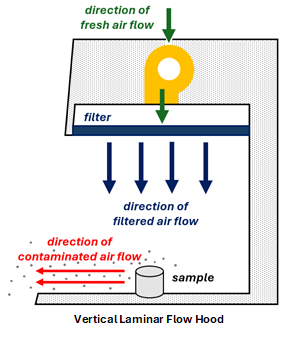
Laminar Flow Hoods
Laminar flow hoods are commonly used to prevent the contamination of sensitive samples. Laminar flow hoods can either have air flow vertically or horizontally but in both instances the air flow is toward the user and the air is exhausted into the laboratory.
Since laminar flow hoods exhaust contaminated air towards the user they are not suitable for handling hazardous or biohazardous materials.